

In contrast to the well-established cognitive benefits of regular MVPA in children, the influence of acute high intensity exercise on cognitive performance requires further examination. (2011) demonstrated that 40 min/day of moderate-vigorous intensity aerobic exercise brought about higher scores on a cognitive assessment of planning ability compared with a control sedentary group of children performing only 20 min/day of activity.
#Bakward digit span test pdf trial
For example, in a trial of 171 sedentary, overweight middle-school children, Davis et al.
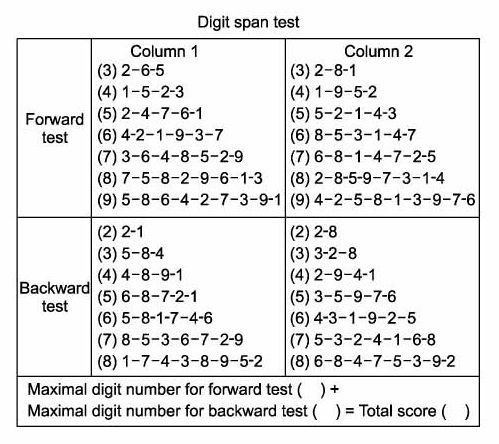
Executive functioning involves cognitive function such as scheduling, planning, response inhibition, working memory, controlled processing, visuospatial processing, and speeded processing ( Best, 2010 Tomporowski et al., 2008, 2011). These studies indicated that most gains of moderate intensity exercise can be seen in executive functioning. Studies of the relationship between exercise and cognition have used various tests measuring global processing (e.g., intelligence and academic achievement) as well as specific components of cognition (e.g., memory and executive function). (2011), cognition is a general term reflecting different processes, including perception, attention, memory, working memory, pattern recognition, executive function, concept formation and reasoning, intelligence, and academic achievement. Specifically, most studies suggested that single bouts of MVPA and participation in PA interventions benefit children’s mental functioning.Īccording to Tomporowski et al. A more recent review of the literature on the effects of PA on children’s cognitive function (64 studies) and academic achievements (73 studies) also reported positive effects ( Donelly et al., 2016). A meta-analysis of 44 studies found a positive, yet weak, correlation (a general effect size of d = 0.32) between PA and different measures of cognitive performance, such as IQ, academic achievements, math and verbal tests, and perceptual skill tests in children ( Sibley and Etnier, 2003). Such programs typically involve daily moderate-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) of 20-60 minutes duration, sufficient to increase cardiorespiratory fitness in children. Interventional studies have further demonstrated the effect of a PA program on cognitive performance in children ( Davis et al., 2011 Hillman et al., 2014). A number of observational studies in children have shown a positive correlation between PA, or physical fitness, and academic achievements ( Carlson et al., 2008 Singh et al., 2012 Tomporowski, 2003 Tomporowski et al., 2008). It is well established that physical activity (PA) and planned exercise have significant health benefits in numerous physical, mental and social aspects ( Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee, 2008 Strong et al., 2005). Parents, educators and coaches should consider these changes in memory and attention following high-intensity exercise activities in children. Cognitive functions applying short term memory improve following a recovery period. Maximal intensity exercise in children and adolescents may result in both beneficial and detrimental cognitive effects, including transient impairment in verbal learning. The DSST test scores were mildly elevated from post-exercise to after recovery. There was a significant decrease in RAVLT scores post-exercise, which returned to baseline values after recovery. Forward and Backward Digit Span scores significantly improved post-recovery compared with baseline measurements. Forward and Backward Digit Span tests, the Rey Auditory-Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT) and the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) were performed at baseline, immediately after, and one hour after a maximal cardiopulmonary exercise test. Using a repeated-measures design, 20 children and adolescents aged 8-17 years completed a battery of tests measuring memory and attention. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of maximal intensity exercise on cognitive performance of children. High intensity physical exercise has previously been found to lead to a decline in cognitive performance of adults.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
