
.png)
The resulting Na + and Cl − ions form a three-dimensional solid that is held together by attractive electrostatic interactions.
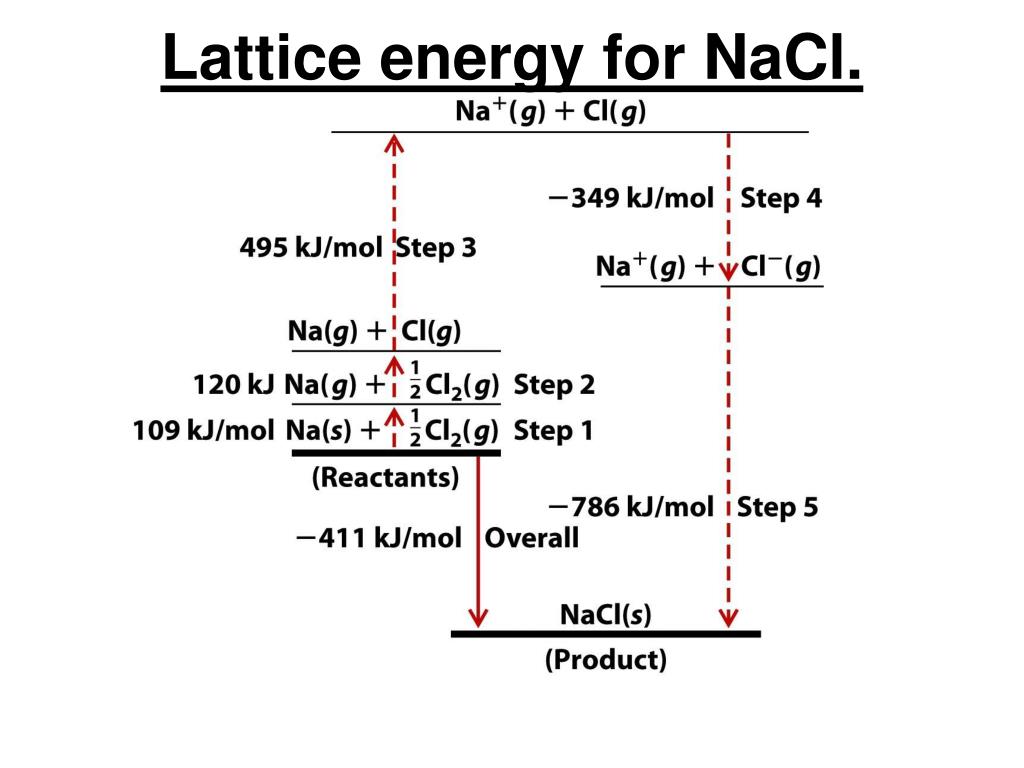
NaCl) instead of a molecular formula to represent the unit cell, and thus the simplest whole number ratio of elements present in the crystal lattice.įigure 9.2.2.The ionic compound NaCl forms when electrons from sodium atoms are transferred to chlorine atoms. Therefore, since it is impossible to define a “molecule” of an ionic compound, we use an empirical formula (e.g.

Sodium chloride, for example, consists of a regular arrangement of equal numbers of Na + cations and Cl – anions ( Figure 9.2.2). This results in the ions arranging themselves into a tightly bound, three-dimensional lattice structure. The attractive forces between ions are isotropic-the same in all directions-meaning that any particular ion is equally attracted to all of the nearby ions of opposite charge. It is incorrect to refer to a sodium chloride (NaCl) “molecule” because there is not a single ionic bond, per se, between any specific pair of sodium and chloride ions. It is important to note, however, that the formula for an ionic compound does not represent the physical arrangement of its ions. (credit a: modification of work by “Jurii”/Wikimedia Commons) (c) When combined, they form white crystals of sodium chloride (table salt). (a) Sodium is a soft metal that must be stored in mineral oil to prevent reaction with air or water. Chlorine is poisonous, but sodium chloride is essential to life sodium atoms react vigorously with water, but sodium chloride simply dissolves in water.įigure 9.2.1.

The compound composed of these ions exhibits properties entirely different from the properties of the elements sodium and chlorine. The vigorous reaction between the elements sodium and chlorine forms the white, crystalline compound sodium chloride, common table salt, which contains sodium cations and chloride anions (Figure 9.2.1). Chlorine atoms form chlorine gas, Cl 2, a yellow-green gas that is extremely corrosive to most metals and very poisonous to animals and plants. Sodium atoms form sodium metal, a soft, silvery-white metal that burns vigorously in air and reacts explosively with water. Neutral atoms and their associated ions have very different physical and chemical properties. Once dissolved or melted, ionic compounds are excellent conductors of electricity and heat because the ions can move about freely. Most ionic solids, however, dissolve readily in water. Ionic solids are also poor conductors of electricity for the same reason-the strength of ionic bonds prevents ions from moving freely in the solid state. Ionic solids exhibit a crystalline structure and tend to be rigid and brittle they also tend to have high melting and boiling points, which suggests that ionic bonds are very strong. The properties of ionic compounds shed some light on the nature of ionic bonds. A cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell.Ĭompounds composed of ions are called ionic compounds (or salts), and their constituent ions are held together by ionic bonds: electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged cations and anions. As you have learned, ions are atoms or molecules bearing an electrical charge.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
